-
Finding the disease persisting in ocean sand means dredging, hurricanes and other things that stir up the ocean floor can spread the disease.
-
Wildlife managers have warned that as warming waters change where fish and other marine life live, existing conservation efforts will become less effective.
-
In an on overview published ahead of its full report, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration said that 2021 ranked the third costliest on record for such events.
-
The ongoing mapping has included Miami, Fort Lauderdale and West Palm Beach. NOAA hopes to enlist more groups to expand the effort.
-
The climate pattern known as La Niña generally brings winters that are drier and warmer than usual across the southern U.S. and cooler and wetter in the northern part of the country.
-
This includes its biggest grant ever: $30 million from NOAA.
-
The map shows predicted red tide affects along Florida's west coast in three-hour increments, based on wind speed and direction.
-
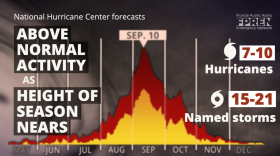
More than two-thirds of the accumulated energy of all tropical storms, hurricanes, and major hurricanes occur between Aug. 15 and Oct. 15 in the Atlantic Basin, including the Gulf of Mexico and the Caribbean Sea.
-
Scientists say the area of little-to-no oxygen is about the size of Lake Ontario and Lake Erie put together.
-
St. Petersburg faces the highest long-term projection of flooding days of any of the 15 cities in Florida cited by the report.
-
For more than five years, a disease has been wiping out corals that provide the foundation for Florida's reef tract. Now it's reached the most remote and healthy area of the reef.
-
Most forecasters say 2021 is shaping up to be another above-normal season, but likely not as busy as the record breaking 2020 hurricane season.
Play Live Radio
Next Up:
0:00
0:00
Available On Air Stations